Shoulder Bursitis: Causes, Symptoms, Treatment & Prevention
October 21, 2025Shoulder bursitis is a common condition that affects the fluid-filled sacs (bursae) in your shoulder, leading to pain, stiffness, and limited movement. Proper understanding of the condition, its causes, symptoms, treatment options, and prevention strategies can help patients manage discomfort and maintain shoulder health.
What Is Shoulder Bursitis?
The shoulder contains several bursae, small fluid-filled sacs that act as cushions between bones, tendons, and muscles. They reduce friction during shoulder movement. Bursitis occurs when one or more of these bursae become inflamed, usually in the subacromial bursa located just above the rotator cuff tendons.
Inflammation can result from repetitive motion, injury, or underlying medical conditions, and if left untreated, it may lead to chronic pain or impaired mobility.
Causes of Shoulder Bursitis
Shoulder bursitis can be caused by a variety of factors:
1. Repetitive Motion
Activities that require frequent overhead movements—such as painting, swimming, or throwing—can irritate the bursa over time, leading to inflammation.
2. Shoulder Injury or Trauma
A fall, blow, or sudden jerking motion can damage the bursa or surrounding tissues, triggering bursitis.
3. Age-Related Degeneration
As people age, the tendons and bursae in the shoulder become less flexible and more prone to irritation and inflammation.
4. Underlying Health Conditions
Certain conditions, including rheumatoid arthritis, gout, and diabetes, increase the risk of developing bursitis.
5. Infection
Although rare, bacterial infection in the bursa (septic bursitis) can cause severe shoulder pain, swelling, and fever.
Symptoms of Shoulder Bursitis
Common signs and symptoms include:
- Pain on the outer shoulder, often worsening when lifting the arm overhead or lying on the affected side
- Swelling and tenderness around the shoulder
- Reduced range of motion or stiffness
- Pain that worsens at night, interfering with sleep
- Warmth or redness in cases of infection
Pain is typically gradual but may intensify with activity, especially movements involving overhead lifting or throwing.
Diagnosing Shoulder Bursitis
A healthcare provider usually performs a physical exam to identify pain points, swelling, and limitations in shoulder movement. Diagnostic tests may include:
- X-rays – to rule out bone spurs or other joint problems
- Ultrasound – to visualize fluid buildup in the bursa
- MRI – for more detailed imaging of soft tissues and inflammation
- Blood tests or aspiration – in suspected cases of infection
Treatment for Shoulder Bursitis
Treatment depends on the severity of inflammation and whether an underlying condition is contributing to the bursitis.
1. Conservative (Non-Surgical) Treatment
Most cases respond well to conservative care:
- Rest and Activity Modification: Avoid movements that aggravate the shoulder.
- Ice Therapy: Apply ice packs several times daily to reduce swelling.
- Physical Therapy: Stretching and strengthening exercises improve mobility and reduce stress on the bursa.
- Medications: Over-the-counter anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) like ibuprofen can help manage pain.
- Corticosteroid Injections: In some cases, an injection into the bursa reduces inflammation and accelerates healing.
2. Surgical Treatment
Surgery is rarely required but may be considered for:
- Chronic bursitis not responding to conservative treatment
- Recurrent shoulder inflammation affecting daily function
- Removal of bone spurs or severely damaged bursa tissue
Can Shoulder Bursitis Be Prevented?
Yes, there are several strategies to reduce the risk of developing bursitis:
- Warm up and stretch before physical activity
- Strengthen shoulder and upper back muscles to support proper joint mechanics
- Avoid repetitive overhead activities or take breaks to reduce strain
- Use ergonomic tools or modifications during work or sports
- Maintain a healthy weight to reduce stress on joints
Early attention to shoulder discomfort and gradual strengthening exercises can significantly lower the risk of bursitis.
Final Thoughts
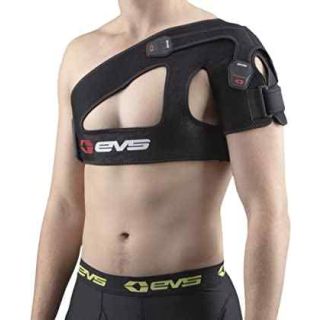
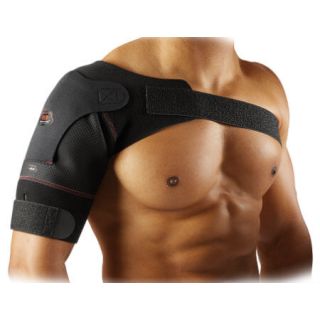
Shoulder bursitis is a common yet manageable condition. Recognizing the causes and symptoms, seeking early treatment, and incorporating preventative strategies can help reduce pain, restore shoulder mobility, and prevent future flare-ups. For ongoing support during recovery, shoulder braces, slings, and compression wraps may help reduce strain and protect inflamed tissues.