Shoulder Arthroscopy: Procedure, Benefits, Risks & Recovery
October 15, 2025Shoulder arthroscopy is a minimally invasive surgical technique used to diagnose and treat various shoulder problems. Using a small camera and specialized instruments, surgeons can repair damaged tissues with less pain, smaller incisions, and faster recovery compared to traditional open surgery.
When is Arthroscopic Shoulder Surgery Used?
Shoulder arthroscopy is commonly performed when nonsurgical treatments—such as rest, physical therapy, or injections—fail to relieve shoulder pain or restore function. The procedure allows surgeons to directly visualize and repair problems inside the shoulder joint.
Common conditions treated with arthroscopic shoulder surgery include:
- Rotator cuff tears – Repairing torn tendons that attach to the humerus.
- Shoulder impingement – Removing inflamed tissue or bone spurs that pinch tendons.
- Labral tears (SLAP or Bankart lesions) – Repairing the cartilage rim that stabilizes the shoulder.
- Shoulder instability – Tightening ligaments or reattaching the labrum to prevent dislocations.
- Frozen shoulder (adhesive capsulitis) – Releasing stiffened joint capsule tissue.
- Shoulder Arthritis or cartilage damage – Cleaning out loose fragments or smoothing rough surfaces.
In some cases, shoulder arthroscopy is also used to evaluate unexplained shoulder pain when imaging studies are inconclusive.
How is Shoulder Arthroscopy Performed?
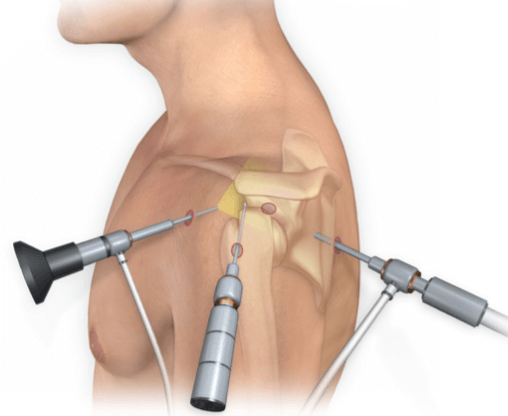
The procedure is typically done under regional or general anesthesia. The surgeon makes several small incisions (about ¼ inch each) around the shoulder to insert the arthroscope (a tiny camera) and specialized surgical tools.
During the operation:
- The joint is filled with sterile fluid to improve visibility.
- The arthroscope transmits images to a video monitor, allowing the surgeon to inspect the joint.
- Depending on the diagnosis, the surgeon may remove inflamed tissue, shave bone spurs, repair tendons, or tighten ligaments.
- Once the repair is complete, the instruments are removed, and the incisions are closed with sutures or surgical tape.
The procedure usually lasts between 30 minutes and 2 hours, depending on the complexity of the repair.
Benefits of Arthroscopic Shoulder Surgery
Arthroscopic surgery offers several advantages over traditional open techniques:
- Smaller incisions and less tissue damage
- Reduced post-operative pain and swelling
- Lower risk of infection and scarring
- Faster recovery and return to activity
- Improved diagnostic accuracy using high-definition visualization
Because of these benefits, arthroscopy is often the preferred approach for treating shoulder injuries in athletes and active individuals.
Risks and Possible Complications
While shoulder arthroscopy is generally safe, it still carries some risks. Potential complications include:
- Infection or bleeding at the incision sites
- Nerve injury or numbness
- Stiffness or loss of motion
- Blood clots (rare)
- Incomplete pain relief or recurrence of symptoms
Your surgeon will discuss these risks and any condition-specific concerns before surgery.
Post-Surgery Care and Recovery
Recovery after shoulder arthroscopy varies depending on the type of repair performed. Most patients go home the same day. The arm is typically supported in a sling for several days or weeks to protect the joint during early healing.
Rehabilitation is a key part of recovery:
- Early phase: Gentle range-of-motion exercises to prevent stiffness.
- Intermediate phase: Gradual strengthening of the rotator cuff and shoulder muscles.
- Final phase: Return to sports or full activity under medical supervision.
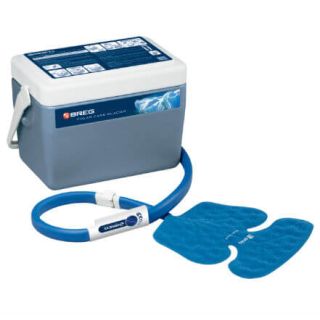
Full recovery can take from 2 to 6 months, depending on the procedure and individual healing rate. Using both a comfortable immobilization sling for shoulder arthroscopy and a cold therapy machine for shoulder surgery can help protect the joint and enhance comfort during your recovery.
Shoulder Cold Therapy Machines
Shoulder Arthroscopy Slings
Conclusion
Shoulder arthroscopy is an effective and minimally invasive solution for a wide range of shoulder problems—from rotator cuff tears to chronic instability. With proper surgical care and rehabilitation, most patients regain strength, flexibility, and pain-free movement within a few months.
If your orthopedic specialist has recommended shoulder arthroscopy, understanding the procedure and recovery process can help you prepare for a successful outcome.